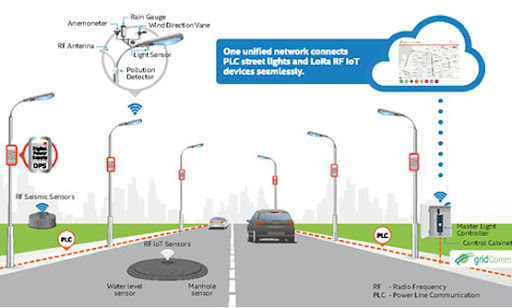
In the rapidly evolving landscape of urban development, the role of technology is becoming increasingly pronounced. Among the myriad advancements aimed at enhancing urban living, the synchronization of street light control networks stands out as a significant innovation with far-reaching implications. As cities grapple with the challenges of sustainability, efficiency, and safety, the implementation of synchronized street light control networks emerges as a compelling solution that promises to revolutionize the urban experience.
The Evolution of Urban Lighting
The concept of street lighting is as old as civilization itself, dating back to ancient times when oil lamps and torches illuminated the pathways of early cities. Over the centuries, advancements in technology led to the proliferation of gas lamps, followed by electric streetlights in the late 19th century. These innovations not only extended the hours of activity within cities but also played a crucial role in enhancing safety and security.
However, traditional street lighting systems were largely static and inefficient. They operated on fixed schedules or rudimentary timers, often resulting in unnecessary energy consumption and light pollution. As urban populations burgeoned and environmental concerns gained prominence, the need for more sophisticated lighting solutions became apparent.
Enter Smart Street Lighting
The emergence of smart technologies has ushered in a new era of urban illumination. Smart street lighting systems leverage a combination of sensors, connectivity, and data analytics to optimize energy usage, enhance visibility, and minimize environmental impact. By integrating these technologies into existing infrastructure, cities can achieve significant improvements in efficiency and functionality.
At the heart of smart street lighting lies the concept of synchronization. Rather than operating as independent entities, individual light fixtures are interconnected within a network that allows for centralized control and coordination. This synchronization enables dynamic adjustments based on real-time conditions, such as traffic patterns, weather events, and pedestrian activity.
The Benefits of Synchronization
The synchronization of street light control networks offers a multitude of benefits, spanning environmental, economic, and social domains.
1. Energy Efficiency:
By synchronizing street lights to operate in concert, cities can reduce overall energy consumption significantly. Dynamic dimming and scheduling algorithms ensure that lights are only illuminated when and where they are needed, minimizing waste and conserving resources.
2. Cost Savings:
The energy savings achieved through synchronization translate into tangible cost savings for municipalities. By reducing electricity bills and maintenance expenses, cities can allocate resources more effectively towards other pressing needs, such as infrastructure upgrades and community services.
3. Enhanced Safety:
Well-lit streets contribute to a safer urban environment by reducing the risk of accidents, crime, and vandalism. Synchronized street lighting ensures consistent illumination levels across different areas, eliminating dark spots and enhancing visibility for both motorists and pedestrians.
4. Reduced Light Pollution:
Excessive artificial light at night not only wastes energy but also disrupts natural ecosystems and impairs human health. Synchronized street lighting systems employ precise controls to minimize light spillage and glare, preserving the nocturnal environment while maintaining adequate visibility.
5. Smart Functionality:
Beyond basic illumination, synchronized street light control networks can support a range of smart functionalities. Integration with traffic management systems, for example, enables dynamic adjustments to light timing based on traffic flow, reducing congestion and emissions.
Implementing Synchronization: Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of synchronized street lighting are clear, the path to implementation is not without challenges. Cities must navigate technical, logistical, and regulatory hurdles to deploy and maintain these advanced systems effectively.
1. Infrastructure Compatibility:
Many cities have existing street lighting infrastructure that may not be compatible with smart technologies. Retrofitting older fixtures with sensors and connectivity modules can be costly and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and coordination.
2. Data Security and Privacy:
The proliferation of sensors and data collection mechanisms raises concerns about privacy and data security. Cities must implement robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with regulations governing data usage and privacy.
3. Interoperability:
Effective synchronization requires seamless interoperability between different hardware and software components. Standardization efforts aimed at defining common protocols and interfaces are essential to ensure compatibility and interoperability across diverse systems.
4. Community Engagement:
Successful implementation of synchronized street lighting hinges on community engagement and stakeholder participation. Cities must involve residents, businesses, and other relevant parties in the planning and decision-making process to ensure that the system meets the needs and expectations of the community.
Case Studies in Synchronization
Several cities around the world have already embraced synchronized street lighting as part of their urban development strategies. These case studies offer valuable insights into the benefits, challenges, and best practices associated with the implementation of synchronized street light control networks.
1. Barcelona, Spain:
Barcelona has emerged as a pioneer in smart city initiatives, including the implementation of synchronized street lighting systems. By deploying sensor-equipped LED fixtures connected to a centralized control platform, the city has achieved significant energy savings while enhancing safety and visibility in public spaces.
2. Los Angeles, USA:
Facing challenges related to traffic congestion and air quality, Los Angeles has invested in a comprehensive smart street lighting program. Through the deployment of synchronized LED fixtures equipped with environmental sensors and adaptive controls, the city aims to improve traffic flow, reduce emissions, and enhance the quality of life for residents.
3. Singapore:
Singapore’s commitment to sustainability and innovation is reflected in its ambitious smart city initiatives. The city-state has deployed synchronized street lighting systems integrated with advanced sensors and analytics capabilities to optimize energy usage, enhance safety, and support urban planning efforts.
The Future of Urban Illumination
As cities continue to grow and evolve, the importance of synchronized street lighting will only increase. Advances in technology, coupled with greater awareness of environmental and societal challenges, will drive further innovation in urban illumination.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see continued investments in smart street lighting infrastructure, along with the development of new applications and services enabled by interconnected lighting networks. From adaptive lighting schemes that respond to real-time events to augmented reality overlays that enhance the urban experience, the possibilities are limited only by our imagination.
In conclusion, the synchronization of street light control networks represents a transformative opportunity for cities to enhance sustainability, efficiency, and safety. By harnessing the power of smart technologies, municipalities can create vibrant, livable urban environments that benefit residents, businesses, and the planet alike. As we illuminate the path forward, let us embrace the potential of synchronized cityscapes to shape a brighter future for all.